Retrieving overpolished fiber-optic connectors
Mike A. Reed, Methode Electronics Inc.
Problem
The problem of overpolishing fiber-optic connectors, specifically those with ceramic ferrules, is a common one, and can often be as damaging to the connector`s performance as underpolishing. Overpolishing typically occurs when coarse lapping film--12-micron in texture or more--is used excessively when removing epoxy from the connector`s ferrule tip. Standard alumina-oxide lapping film can remove glass and epoxy but not ceramic. As a result, the fiber surface can be undercut below the ferrule surface when overpolished.
Solution
Connector manufacturer`s guidelines must be followed during polishing to achieve the desired finish. Still, there is no substitute for practice to ensure good results. If overpolishing occurs, the only effective way to retrieve the ceramic connector is to cut back the ceramic ferrule surface and repolish the glass.
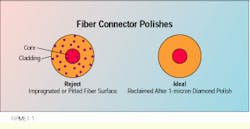
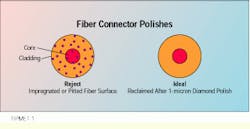
You can determine if there is overpolishing when you view the fiber endface through a microscope prior to power-loss testing. After a rough polish, the fiber finish will be saturated with pits and scratches that can cause higher than acceptable optical loss. These defects appear as small speckles and spots in and around the core-cladding region of the fiber.
Procedure
Follow all the manufacturer`s steps for terminating and polishing. If after the final step--usually polishing with 0.3-micron alumina-oxide film--speckles or spots are apparent, take the following steps:
1) Place a sheet of 1-micron diamond lapping film on a resilient pad, and add several small drops of distilled water.
2) Perform approximately 10 figure-eight polishing motions with the connector placed in a handheld polishing disk.
3) Clean the surface of the connector with isopropyl alcohol and visually inspect.
The diamond paper will cut back a small amount of the ceramic ferrule, allowing access to the surface of the glass. With a 1-micron diamond polish, the impregnated surface of the fiber should be reclaimed, resulting in lower decibel loss. Also, minimizing the need to replace connectors saves time, money and resources.
Reject a fiber endface that, after polishing, shows an impregnated or pitted surface. Reclaim the surface with a 1-micron diamond polish.
Mike A. Reed is responsible for all fiber-optic training and field applications at Methode Electronics Inc., Chicago.