With trends pointing to pre-terminated solutions, optical systems provide advantages and benefits in data center environments.
It is predicted that within the next five years, the data center will become the largest opportunity for fiber-optic systems in the entire premises market (Structured Cabling Systems Market: 2005, FTM Consulting). The increase in bandwidth-hungry applications, the demand for higher density, and concerns over reliability are fueling the preference of fiber optics in this environment.
Beyond satisfying data center performance requirements, fiber-optic systems have begun to shake the perception of being a more-expensive approach to networking. The IEEE (802.3ae) has standardized on a 50-µm core multimode fiber for 10-Gbit/sec Ethernet applications. Vertical-cavity surface-emitting laser (VCSEL)-based multimode modular transceivers used for 1-Gbit/sec serial transmission are now on par or less expensive than their copper counterparts. This same low-cost multimode transceiver technology is also used in 10-Gbit/sec systems, and is being considered for the next-generation 40- to 100-Gbit/sec Ethernet systems. This creates a simple upgrade path for future bandwidth requirements without a media retrofit.
Fiber-optic cabling systems deployed in the data center have also evolved in response to the unique demands of mission-critical applications. Quick fiber-optic connectivity deployment methods are becoming increasingly popular, offering higher reliability than traditional field-installed methods. These solutions provide a compact cabling footprint, as many fibers can be consolidated into a single, pre-terminated cabling element.
The requirement for scalability is met by the solution’s ability to be deployed very rapidly and with each component designed to be intermateable and interchangeable. The densities of these solutions, along with their modularity, give them great flexibility and increased manageability.
Optical-fiber systems require a transceiver to convert electrical data to an optical signal in a switch or interface. Concerns over cost, module size, and transceiver power consumption were some of the factor inhibiting widespread fiber-optic deployment. But with the advent of VCSEL devices, transceiver manufacturers have addressed these areas by reducing the module size, power consumption, and cost of gigabit-speed optical components.
High-speed multimode transceivers (described as Physical Medium Dependent or PMDs) use an 850-nm wavelength VCSEL as an emitter. Since these transceivers have become the de facto standard, the cost of a 1-Gbit transceiver has declined dramatically; 1-Gbit network interface cards (NICs) are available for $30, while 10-Gbit devices, which have been commercialized using similar VCSEL technology, should follow a similar price-reduction path.
Trends in interconnect solutions
Demands for reliability, scalability, and manageability are forging the trend away from traditional field-installed connectivity solutions toward a pre-terminated approach to connectivity and media.
The historical method of fiber-optic connectivity deployment consists of a high-fiber-count distribution cable being pulled in place, connectors terminated to the end of the cable, and then mated to a fiber adapter panel that is installed in a fiber enclosure. An alternative method to field termination would be to substitute the connector portion of this solution with a factory-connectorized pigtail that is then attached to the distribution cable by a mechanical or fusion splice.
The reliability and ultimate optical performance of a traditional field-installed connector solution are highly dependent on installer skill and the installation’s environment. It is labor-intensive, time-consuming, and requires the use of specialized equipment by trained installation professionals. In addition, any changes to this system require the same level of labor and skill to complete.
Pre-terminated fiber-optic connectivity solutions, however, consist of trunk cables (pre-terminated with multiple fiber-optic connectors) that are pulled into place and snapped into pre-terminated cassettes or fiber-adapter panels. Factory-terminated cables and cassettes eliminate the intrinsic variations associated with performing field terminations.
Using 12-fiber array connectors on the trunk cable and the similarly equipped pre-terminated cassettes let you connect multiple fibers quickly in a very small space. This method also eliminates the need for tools or specialized training to facilitate installation. The pre-terminated method is highly scaleable because the cassettes can be added or changed to accommodate different connector requirements or upgrades. With its low labor cost and ease of installation, a pre-terminated solution shows the largest cost benefit over time. Any moves, adds, or changes can be completed rapidly, with no special skills required.
Opportunities in the data center
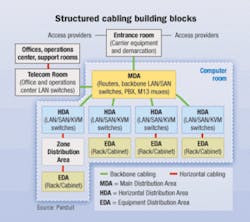
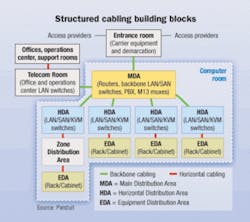
The Telecommunications Infrastructure Standard for Data Centers (TIA-942) specifies requirements and guidelines for design and installation of data center telecommunications cabling. Released in April 2005, this document lays out a consistent system for infrastructure design and development through the use of cabling system “building-block” elements. It is intended for use by data center designers for application to facility planning, network design, and design and specification of the structured cabling system (SCS).
There are nine key cabling elements in the data center as depicted in the TIA-942 logical layout for data centers; however, the main distribution area (MDA) and horizontal distribution areas (HDAs) are the fastest-growing opportunities for fiber-optic systems, and are the leading candidates for pre-terminated quick-deployment products. This is particularly true on the storage area network (SAN) side of the data center, which typically is fiber-rich.
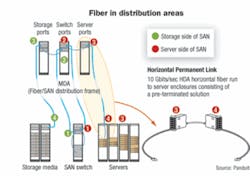
The representation of MDA/HDA connections employing pre-terminated solutions, depicted in the figure “Fiber in distribution areas” (page 24), shows a 10-Gbit/sec 12-fiber cable, along with cassettes, used as the horizontal permanent link between the HDA and server enclosures. Pre-terminated cassettes containing LC connectors are placed in the appropriate enclosure hardware on both ends to complete the horizontal permanent link. LC patch cords are deployed on the patch field of each cassette to complete the channels. If a move is required, the cassettes can be disconnected and relocated to the desired connection point. If a different connector interface is required, the cassette can be replaced with a cassette containing the preferred connector interface. To facilitate higher density, as a result of the addition of more electronics, the system port count can be increased by pulling trunk cables, installing higher-density cassettes, and adding more patch cords.
The TIA/EIA-568-B.1-7 standard provides requirements and guidelines on wiring pre-terminated systems that use array-based connectors. This document is an addendum to TIA/EIA-568-B.1, and instructs readers in three different methods (“A,” “B,” and “C”) for maintaining fiber-connectivity system polarity in systems based on FOCIS-5, 12-fiber array connectors.
The standard seeks to assure interoperability among vendors. When specifying pre-terminated systems, to eliminate confusion after system deployment, it is crucial that you understand early in the design phase the polarity method that is used. It is possible (but not trivial) to mix pre-terminated components that adhere to different wiring methods. To assure consistent interoperability, you should select and maintain one wiring method throughout the data center.
Pre-terminated benefits
Pre-terminated systems offer increased reliability through factory termination, providing verified and documented performance. Time and cost savings are achieved due to the modular design when compared to traditional connectivity systems.
Interoperable components in conformance with the TIA/EIA guidelines minimize confusion and the potential for optical-performance issues. SCS manageability is optimized through cassette patch-field organization, labeling quality, and the deployment of small-form-factor cabling systems (front and rear of the cassette).
A pre-terminated system, of which the Panduit Opticom QuickNet Fiber Optic Cabling System pictured in this article is an example (page 26), enables quick, plug-in network deployment of up to 96 fiber connections in a single rack space with excellent cable access and cable-management capabilities. It enables installation in less than 20% of the time required for traditional field-polish connectors with distribution cables.
Modular pre-terminated cassettes provide a scalable solution for the lowest total cost of ownership. Optimized cassettes can deliver a maximum insertion loss of 0.5 dB per channel. They are 100% tested to deliver verified optical performance and reliability for improved network integrity, allowing for more complex and longer-reach network segments.
A scalable solution
Pre-terminated fiber-optic systems optimize your data center investment by providing a scalable infrastructure that meets today’s requirements, with the flexibility to expand to meet the advanced application needs of tomorrow. 10-Gbit/sec multimode fiber-optic systems allow backward compatibility with a simple upgrade path for future application demands. System modularity enables easy upgrades to extend network lifecycle. Pre-terminated systems provide added benefits by providing factory-terminated and tested connectivity for assured performance and reliability to lower total cost of ownership.ADAM HOUSTON is a business development manager at Panduit Corp. (www.panduit.com).