CommScope, Google team to drive Citizens Broadband Radio Service (CBRS) forward
CommScope and Google announced that the companies are working together to jointly develop, deploy and operate an Environmental Sensing Capability (ESC) network, advancing Citizens Broadband Radio Service (CBRS) technology to market. The joint ESC leverages the technical capabilities of each company with a consolidated footprint – resulting in more places to deploy CBRS and higher availability spectrum for operators of CBRS-based networks.
“This critical network infrastructure agreement represents a major commitment to CBRS by two major SAS providers and will help to ensure that the opportunities presented by CBRS will soon be realized,” said Ben Cardwell, senior vice president, CommScope Mobility Solutions. “Together, we can bring about a combined ESC network faster and more efficiently, leveraging the combined capabilities of two major companies.”
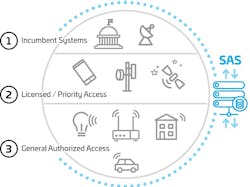
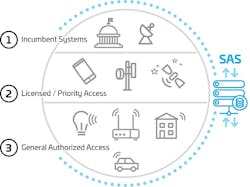
The CBRS band is 150 MHz of 3.5 GHz spectrum, which will be shared by the current incumbents, including federal government radar systems, and new commercial users. CBRS will provide new dynamically-allocated shared spectrum for various use cases such as private networks, fixed wireless access, wireless rural broadband, indoor wireless coverage, the Internet of Things, and additional cellular capacity. The FCC has authorized shared use of the band, which enables the support of commercial wireless services while protecting incumbent use.
CBRS spectrum is managed by Spectrum Access Systems (SASs), which require an ESC network to sense radar operation. The ESC will alert the SASs of naval radar operations, so the connected SAS systems can reconfigure spectrum allocations for nearby CBRS devices to operate without interfering with naval activity.
CommScope and Google will each provide independent SAS services and jointly operate the ESC network. The ESC network is engineered for high availability with the built-in redundancy and fault detection necessary to provide this key enabling capability. As part of this collaboration, both companies share responsibility for overall network design.
Google has developed the ESC sensor and cloud decision engine and will operate the cloud that communicates with each SAS. CommScope will deploy and manage the operation of the physical network. CommScope and Google are working with the FCC and other governmental agencies to obtain certification of the ESC.
“The ESC represents more than a check-the-box capability. To effectively manage spectrum, a SAS relies on accurate ESC notifications - that eliminate false positive readings - from a high availability sensing network,” said Milo Medin, vice president of Wireless Services at Google. “We are excited to work with CommScope toward the success of CBRS.”