Work safely when terminating fiber-optic cable
Michael C. Longo and Randy Clark, Anixter Inc.
INSTALLER TIPS
Problem
Multimode optical-fiber network systems operate at either 850- or 1300-nanometer wavelengths, and singlemode systems operate at 1310 or 1550 nm. All of these ranges are in the infrared scale and outside the visible spectrum. Although optical sources such as light-emitting diodes in fiber-optic networks have a low power level, overexposure to a working fiber may damage your retina.
A second important area of safety concern is handling bare fibers. Fiber-termination procedures include stripping away the protective coating from the core and cladding and exposing the bare fiber. Splinters or scraps can easily penetrate your skin, and they are difficult to find and remove. If these fibers get into your eyes, they are especially difficult to wash out.
Another consideration for safety involves handling epoxies used in many fiber-optic connectors.
Solution
Handling optical fiber is not inherently dangerous; however, there are some dos and don`ts you should follow. Safety is always the top priority in any working environment, and certain precautions should be taken to prevent accidents and injuries. When terminating optical fibers, use common sense, wear proper eye protection, work in an optimum environment (not in a cramped space) and keep the work area clean.
Procedures
1) Protect vision
2) Never look into the end of a fiber to check if it is in operation. If you do look into a working fiber, the light appears to be red, resulting from the fact that the receptors in your retina are being overloaded. Overexposure can lead to permanent eye damage.
3) Always use a fiber-optic power meter to check if a fiber is in operation.
4) When terminating fiber, wear safety glasses with side shields.
5) Don`t touch your eyes when you are working with bare fiber. Wash your hands after handling, especially if you wear contact lenses.
6) Work on a dark surface, to provide contrast for the clear glass fiber.
Account for all bare fiber
Remove any fiber that penetrates the skin; the body cannot dissolve glass. If you do not remove the splinter immediately, you may have to wait until it works itself out, which may prove painful.
To prevent accidental punctures, properly dispose of all bare glass pieces--a safety receptacle is best. If no receptacle is available, place all pieces of glass on a loop of black electrical tape with the adhesive side out. Carefully dispose of these glass pieces.
Keep fiber and work area clean
Do not eat or drink in the work area; ingested fibers can cause internal bleeding.
Never smoke in the work area; smoke and ashes can quickly coat the fiber and can create a fire hazard when adhesives and cleaners are being used.
When working with epoxy--either mixing it with a primer or heat- or UV-curing--keep the fiber and the area clean.
Use an alcohol wipe one time only to clean the fiber, then dispose of wipe properly.
Always wash your hands with soap and water to remove any epoxy. Do not use an alcohol wipe to clean your hands because this will liquefy and spread the epoxy instead of removing it.
Michael C. Longo, Registered Communications Distribution Designer (RCDD), is technical marketing manager, and Randy Clark, RCDD, is marketing manager at Anixter Inc., Skokie IL.
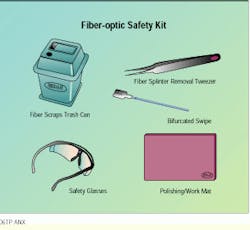
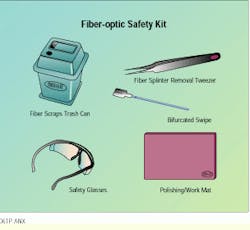
A fiber-optic safety kit might include items such as safety glasses, fiber-scrap can, alcohol swipe, tweezers and a dark-colored polishing work mat.