OCC tackles field testing of direct-attach links
A new white paper from OCC explains how the company has tackled the complicated and less-than-rock-solid task of testing a direct-attach modified permanent link. As we have covered in the past, the direct-attach or modified permanent link topology is one in which a horizontal cable is terminated to a plug—rather than an outlet—at the device end. That plug connects directly to the network device being served; in many cases that device is an IP camera or a wireless access point.
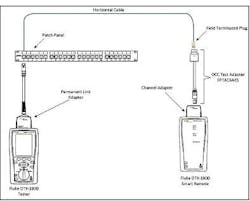
This outside-the-norm topology has prompted a test methodology that also is outside the norm. Typically, a direct-attach link is tested by using the permanent link adapter on the main test unit, and the channel adapter on the remote test unit. The field-terminated plug connects directly to the channel adapter in this setup. However, as OCC points out in its white paper, the tester “excludes the plug connected directly to the channel adapter from the measurement. The test results may pass with good margin even though the plug has been poorly terminated.”
In response to this challenge, the company has developed the OCC Field Plug Test Adapter (pictured immediately below). The company says this adapter “provides installers in the field the capability to accurately measure the true performance of direct-attach links.”
To use the OCC Field Plug Test Adapter, an installer uses the same setup described earlier—permanent-link adapter attached to the main unit and channel adapter attached to the remote unit. One end of the OCC Field Plug Test Adapter plugs into the tester’s channel adapter; the other end of the OCC Field Plug Test Adapter receives the field-terminated plug.
In one experiment, OCC tested a poorly terminated direct-attach link using both setups—with and without the OCC Field Plug Test Adapter. When tested without the adapter, “the link passed the Category 6 test requirements with good margin,” OCC says, because despite the fact it was poorly terminated, the channel adapter cancelled out the plug’s performance. When tested with the adapter, “the measured results [were] clearly much worse and actually fail the Category 6 link test,” OCC says.
The two images shown here come directly from the OCC white paper titled “Field Testing of Direct Attach Modified Permanent Links.” That paper also includes graphical test results of the poorly terminated link generated with and without the use of the adapter. In its paper, OCC concludes, “By utilizing the field plug test adapter, the poorly terminated plug is factored into the measurement and the true performance of the link is recognized.”
About the Author
Patrick McLaughlin
Chief Editor
Patrick McLaughlin, chief editor of Cabling Installation & Maintenance, has covered the cabling industry for more than 20 years. He has authored hundreds of articles on technical and business topics related to the specification, design, installation, and management of information communications technology systems. McLaughlin has presented at live in-person and online events, and he has spearheaded cablinginstall.com's webcast seminar programs for 15 years.